
The best way to evaluate a company’s gross margin percentage is to analyze the trend over time and compare it to peers or the industry average. The gross margin measures the percentage of revenue a company retains after deducting the costs of producing the goods or services it sells. This means that after Jack pays off his inventory costs, he still https://www.bookstime.com/ has 78 percent of his sales revenue to cover his operating costs. Is there software you can use to collect and organize customer information? Can you use tracking software to manage shipping data and customer notifications? Sometimes this is unavoidable; you will need to pay for supplies, website hosting, employee salaries, and many other expenses.
Gross Profit Margin
Margins for the utility industry will vary from those of companies in another industry. The average net profit margin for general retail sits at 2.65%, while the average margin for restaurants is 12.63%. That’s because profit margins vary from industry to industry, which means that companies in different sectors which ratio is found by dividing gross margin by sales? aren’t necessarily comparable. So, for example, a retail company’s profit margins shouldn’t be compared to those of an oil and gas company. Let’s say that two restaurants have each raised $1 million by issuing stock to investors. So restaurant A is earning a higher return on the $1 million in equity.
What Is a Good Profit Margin?
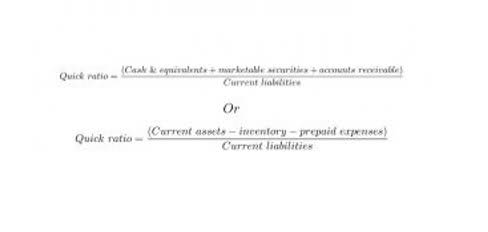
The gross profit percentage formula is calculated by subtracting cost of goods sold from total revenues and dividing the difference by total revenues. Usually a gross profit calculator would rephrase this equation and simply divide the total GP dollar amount we used above by the total revenues. A higher gross profit margin indicates a more profitable and efficient company. However, comparing companies’ margins within the same industry is essential, as this allows for a fair assessment due to similar operational variables. Net profit margin is a key financial metric indicating a company’s financial health. Also known as net margin, it shows the profit generated as a percentage of the company’s revenue.

Gross profit margin ratio: What is it and how to use it
- The COGS margin describes the relationship between a company’s cost of goods sold (COGS) and revenue.
- Gross profit is determined by subtracting the cost of goods sold from revenue.
- Notice that in terms of dollar amount, gross profit is higher in Year 2.
- The gross margin is extremely simple, straightforward to calculate, and provides an instant snapshot of how much revenue is retained after production costs are deducted.
However, such measures may have negative effects such as decrease in sales volume due to increased prices, or lower product quality as a result of cutting costs. Nonetheless, the gross profit margin should be relatively stable except when there is significant change to the company’s business model. The gross profit margin looks at the company’s profitability of production.
New York University analyzed a variety of industries with net profit margins ranging anywhere from about -29% to as high as 33%. For instance, the study showed that the hotel/gaming sector had an average net profit margin of -28.56%, while banks in the money sector had an average net profit margin of 32.61%. The most effective way to increase revenue is to increase sales among your existing customer base. You can also use promotions, rewards, and testimonials to promote your products and increase sales.

Conceptually, the COGS margin ratio represents the percentage of each dollar of revenue generated that is spent on cost of goods sold (COGS). Many businesses regularly eliminate low-performing inventory or change their service offerings. But cutting low performers will lower your costs and increase your sales, which will raise your profit margin as well.
How to Calculate Profit Margin
This is used to show how much revenue is left over after paying variable costs such as wages and raw materials. It is the same as the company’s return on sales, and indicates how well that return is being managed. Businesses subtract their COGS as well as ancillary expenses when calculating net margin and related margins. Some of these expenses include product distribution, sales representative wages, miscellaneous operating expenses, and taxes. Companies use gross margin to measure how their production costs relate to their revenues.

Step 2. Project Cost of Goods Sold Using COGS Margin Ratio

